1. Introduction:
Recruitment is one of the most important functions of Human Resource Management (HRM). It is the process through which organizations identify, attract, and select suitable candidates to fill job vacancies. Choosing the right source of recruitment plays a vital role in building a skilled, motivated, and productive workforce.
Recruitment sources are broadly classified into internal sources and external sources. Internal sources of recruitment focus on filling job vacancies from within the organization itself. This blog provides a detailed explanation of the meaning, types, advantages, and limitations of internal sources of recruitment, along with best practices and a comparison with external recruitment.
2. Meaning of Internal Sources of Recruitment:
Definition of Internal Recruitment
Internal sources of recruitment refer to the process of filling job vacancies by selecting existing employees of the organization. Instead of hiring new candidates from outside, companies promote, transfer, or reassign current employees to higher or different positions.
In simple words, internal recruitment means “hiring from within the organization.”
How Internal Recruitment Works in Organizations
When a vacancy arises, the HR department:
Checks existing employee records
Evaluates skills, performance, and experience
Identifies suitable internal candidates
Fills the position through promotion, transfer, or job rotation
This method encourages employees to grow within the organization.
Examples of Internal Recruitment in Real Workplaces
A senior clerk is promoted to the position of office manager
An employee is transferred from the sales department to marketing
A retired expert is recalled to guide a new project
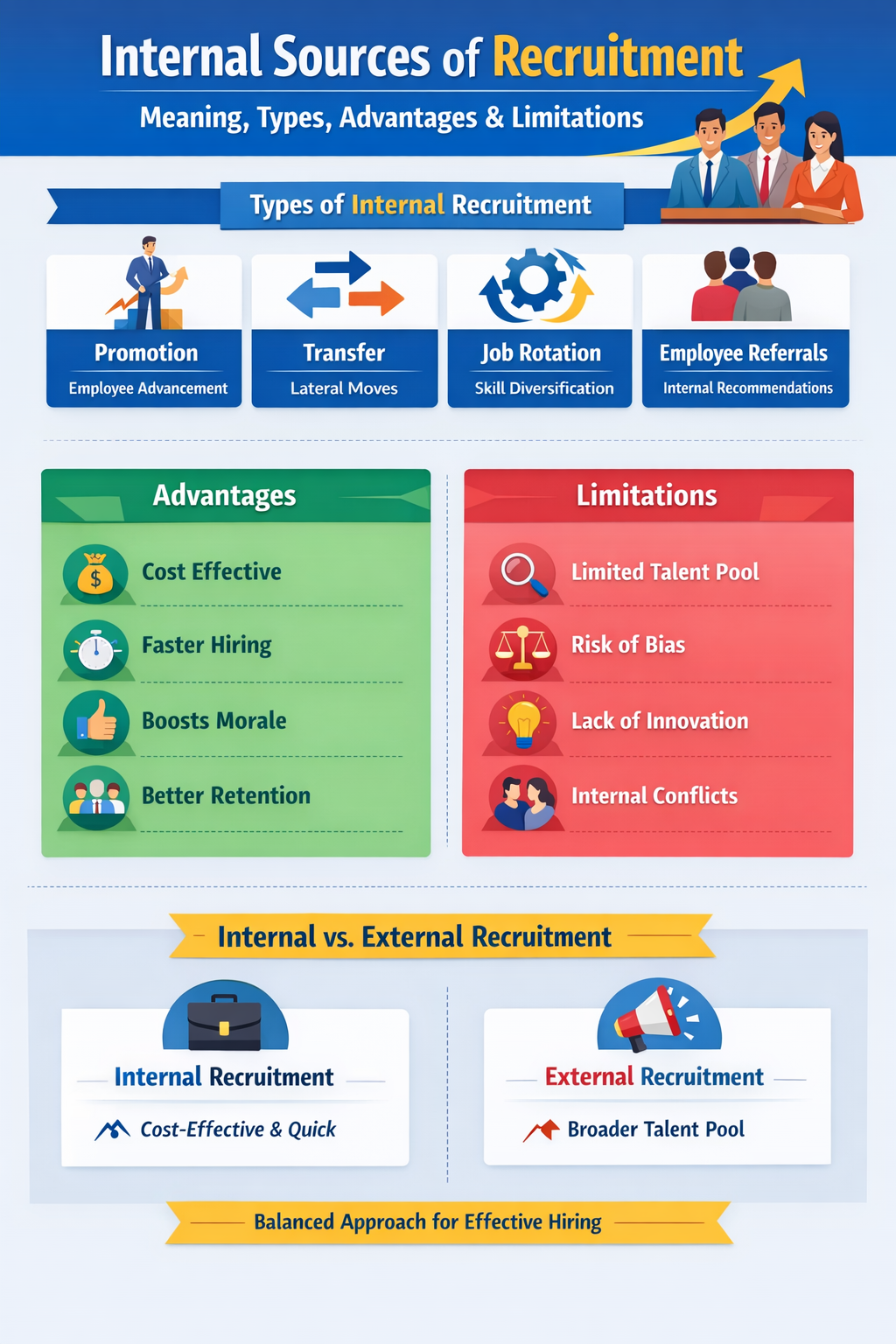
3. Types of Internal Sources of Recruitment
3.1 Promotion
Meaning and Features
Promotion refers to moving an employee to a higher position with greater responsibility, authority, and salary. It is based on performance, experience, and merit.
Features of Promotion:
Higher status and pay
Increased responsibilities
Motivation for employees
Recognition of hard work
Example of Promotion
An assistant manager promoted to the position of branch manager.
When Promotion Is Most Suitable
When leadership skills are required
When employees show consistent performance
When long-term organizational loyalty is valued
3.2 Transfer
Meaning of Transfer
A transfer means shifting an employee from one job to another at the same level without any change in salary or rank.
Types of Transfers
Horizontal Transfer – Same position, different department
Vertical Transfer – Change in position (rare)
Departmental Transfer – Movement within departments
Benefits of Employee Transfer
Reduces job monotony
Balances workforce needs
Enhances employee flexibility
Improves overall efficiency
3.3 Job Rotation
Concept of Job Rotation
Job rotation involves shifting employees from one job role to another periodically to broaden their skills and experience.
Purpose and Scope
Develop multi-skilled employees
Prepare employees for future roles
Reduce boredom and stress
Role in Skill Development
Job rotation helps employees understand different business functions, making them more adaptable and confident.
3.4 Employee Referrals (Internal)
How Internal Referrals Work
Existing employees recommend suitable candidates (often colleagues or known professionals) for job vacancies within the organization.
Advantages for Employer and Employees
Faster hiring process
Reliable candidates
Better cultural fit
Referral rewards motivate employees
3.5 Former Employees / Recall
Re-Hiring Retired or Resigned Employees
Organizations may re-hire retired or previously resigned employees due to their experience and familiarity with the company.
Situations Where Recall Is Useful
Shortage of skilled employees
Emergency projects
Specialized knowledge requirement
4. Advantages of Internal Sources of Recruitment
1. Cost-Effective Recruitment
Internal recruitment saves costs related to advertising, interviews, and onboarding.
2. Faster Hiring Process
Vacancies are filled quickly since employee data is already available.
3. Better Employee Motivation and Morale
Promotions and internal opportunities boost employee confidence and job satisfaction.
4. Reduced Training and Induction Cost
Internal candidates already understand organizational culture and policies.
5. Improved Employee Retention
Career growth opportunities reduce employee turnover.
6. Better Cultural Fit and Performance Predictability
The performance of internal employees is known, reducing hiring risks.
5. Limitations of Internal Sources of Recruitment
1. Limited Talent Pool
The organization may miss out on fresh and innovative talent.
2. Possibility of Internal Conflicts
Employees who are not selected may feel demotivated.
3. Lack of Fresh Ideas and Innovation
Over-dependence on internal hiring can lead to stagnation.
4. Risk of Favoritism or Bias
Unfair promotions may reduce trust in management.
5. Creates Vacancies at Lower Levels
Promoting one employee creates another vacancy.
6. Internal Sources of Recruitment vs External Sources (Brief Comparison)
| Basis | Internal Recruitment | External Recruitment |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low | High |
| Time | Fast | Time-consuming |
| Motivation | High | Moderate |
| Talent Pool | Limited | Wide |
| Innovation | Limited | High |
When Internal Recruitment Is More Suitable
For leadership positions
When employee morale is a priority
When time and cost are limited
When External Recruitment Becomes Necessary
For new skills and ideas
During expansion
When internal talent is unavailable
7. Best Practices for Using Internal Recruitment Effectively
Transparent promotion policies
Fair and unbiased performance appraisal
Skill mapping and succession planning
Balanced use of internal and external sources
Combining both methods ensures long-term organizational growth.
8. Conclusion
Internal sources of recruitment play a crucial role in employee development, motivation, and organizational stability. Methods such as promotion, transfer, job rotation, employee referrals, and recall help organizations utilize existing talent efficiently.
However, internal recruitment should not be the only strategy. A balanced approach combining internal and external recruitment ensures innovation, competitiveness, and sustainable growth.
Strategic HR planning requires selecting the right recruitment source at the right time to achieve organizational success.