1. Introduction
The rapid rise of Generative AI in cybersecurity
has transformed how organizations detect threats, respond to incidents, and
automate security operations. From AI-driven threat intelligence to automated
incident response, generative AI models are redefining modern cyber defense
strategies.
However, while the benefits of generative AI are
widely discussed, understanding the risks and challenges of using Generative
AI in cybersecurity is equally critical. Overlooking these risks can lead
to data breaches, compliance violations, and flawed security decisions.
This article explores the key risks, challenges,
and limitations of Generative AI in cybersecurity, covering technical,
ethical, legal, and operational concerns while also offering best practices for
responsible adoption.
2. What Is Generative AI in
Cybersecurity?
Generative AI refers to advanced AI models, such as
large language models (LLMs), that can generate text, code, images, and
patterns based on training data. In cybersecurity, these models are used to
analyze logs, generate security reports, simulate attacks, and assist security
analysts.
Common cybersecurity use cases include:
- Threat
detection and alert triage - Automated
incident response recommendations - Malware
analysis and code review - Phishing
detection and security awareness training
Organizations are rapidly adopting Generative AI to
improve efficiency in Security Operations Centers (SOCs), reduce
response time, and handle the growing volume of cyber threats.
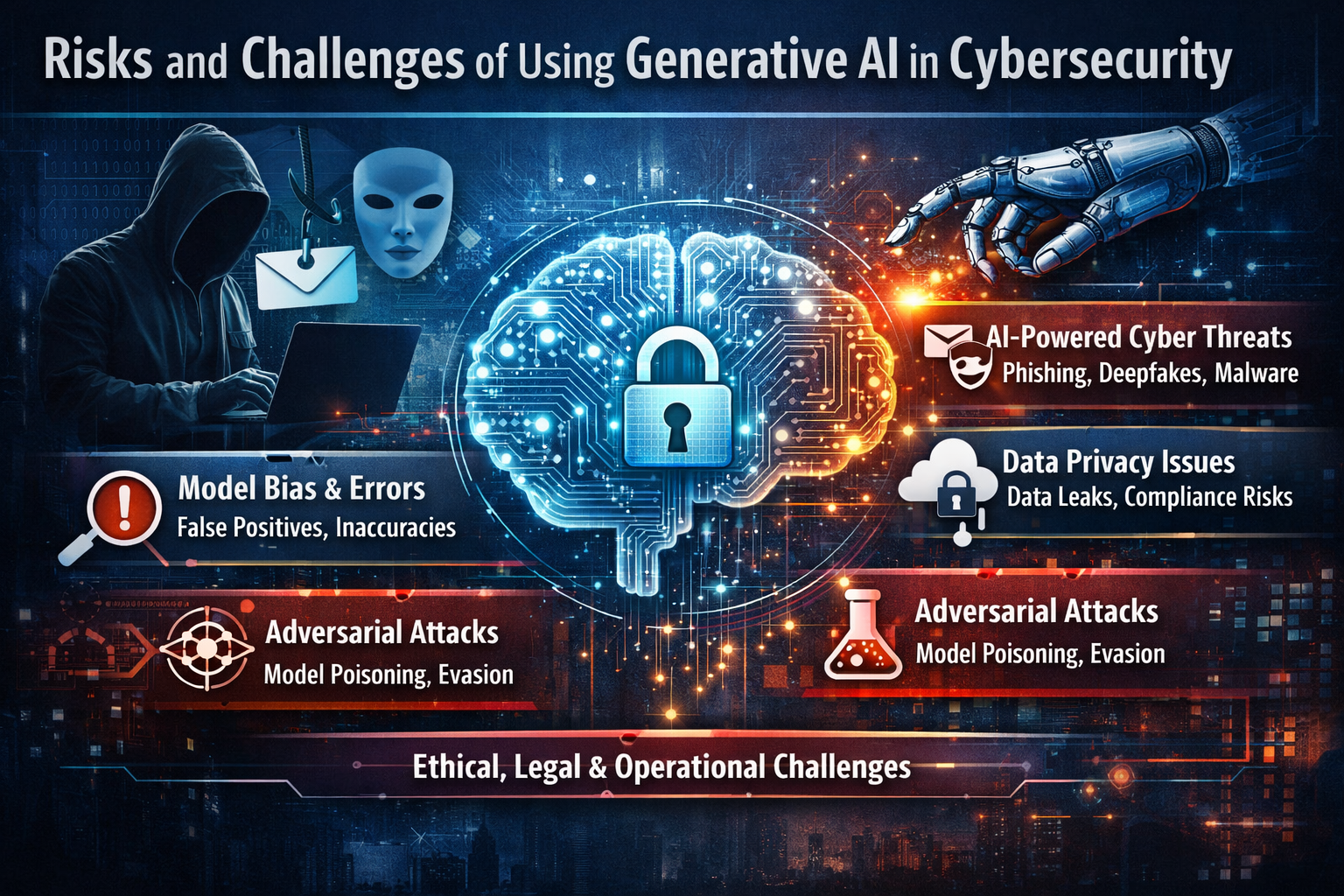
3. AI-Powered Cyber Threats
While AI strengthens defense mechanisms, attackers
are also using AI to launch more sophisticated cyber attacks.
AI-generated phishing and social
engineering attacks
Generative AI can create highly convincing phishing
emails, messages, and voice scripts that mimic human language, making them
harder to detect.
Deepfakes and identity impersonation
AI-powered deepfakes enable attackers to impersonate
executives or employees, leading to financial fraud and unauthorized access.
Automated malware creation
Generative AI can help cybercriminals rapidly
generate malware variants, making traditional signature-based detection less
effective.
4. Data Privacy & Confidentiality
Risks
One of the biggest concerns in using Generative AI
in cybersecurity is data privacy.
Training models on sensitive data
AI models often require large datasets that may
include confidential logs, credentials, or personal information.
Data leakage through AI prompts and
outputs
Improper prompt handling can lead to unintended
disclosure of sensitive information through AI-generated responses.
Compliance challenges (GDPR, ISO, SOC)
Using AI systems can complicate compliance with
regulations such as GDPR, ISO 27001, and SOC 2, especially when data
usage and storage lack transparency.
5. Model Bias, Hallucinations & Accuracy
Issues
Generative AI systems are not always accurate or
unbiased.
False positives and false negatives
AI-driven security tools may incorrectly flag
legitimate activity or miss real threats, leading to alert fatigue or
undetected breaches.
Hallucinated threats or missed attacks
AI hallucinations can generate false threat
narratives, while genuine attacks may go unnoticed due to flawed training data.
Impact on incident response decisions
Relying on incorrect AI recommendations can delay
response time and worsen the impact of cyber incidents.
6. Over-Reliance on AI Systems
Excessive dependence on AI introduces serious
operational risks.
Reduced human oversight
When security teams trust AI blindly, critical
judgment and contextual understanding may be lost.
Automation risks in SOC operations
Fully automated responses can unintentionally block
legitimate users or disrupt business operations.
Importance of human-in-the-loop models
Combining AI automation with human validation
ensures better accuracy, accountability, and decision-making.
7. Adversarial Attacks on AI Models
AI systems themselves are becoming targets.
Prompt injection attacks
Attackers manipulate prompts to bypass safeguards
and extract sensitive information from AI systems.
Model poisoning
Corrupting training data can cause AI models to
behave unpredictably or provide malicious outputs.
Evasion techniques targeting AI systems
Attackers design inputs specifically to evade
AI-based detection mechanisms.
8. Ethical & Legal Challenges
The ethical use of Generative AI in cybersecurity
remains a major concern.
Accountability for AI-driven decisions
Determining responsibility for AI-based security
failures is complex.
Transparency and explainability issues
Many AI models operate as “black boxes,” making it
difficult to explain how decisions are made.
Legal liability concerns
Organizations may face legal consequences if
AI-driven actions cause data breaches or regulatory violations.
9. Integration & Operational
Challenges
Deploying Generative AI is not always seamless.
Compatibility with existing security
tools
AI solutions may not integrate well with legacy
SIEM, SOAR, or endpoint security systems.
Skill gaps in AI-enabled security teams
Cybersecurity professionals need AI literacy to
effectively manage and interpret AI outputs.
Infrastructure and cost constraints
AI systems require high computing power, secure
infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance, increasing operational costs.
10. Managing Risks: Best Practices &
Mitigation Strategies
Organizations can reduce risks by following
structured approaches.
Secure AI deployment frameworks
Adopt zero-trust principles, secure APIs, and
controlled AI access.
Data governance and access controls
Ensure sensitive data is anonymized, encrypted, and
accessed on a need-to-know basis.
Continuous monitoring and validation
Regularly test AI outputs for accuracy, bias, and
anomalies.
Regular audits and compliance checks
Conduct security audits and align AI usage with
regulatory requirements.
11. Role of Policy, Regulation &
Standards
Regulation plays a key role in responsible AI
adoption.
Emerging AI governance frameworks
Governments and organizations are introducing
AI-specific cybersecurity guidelines.
Organizational policies for AI use
Clear internal policies help define acceptable AI
usage, accountability, and risk tolerance.
Future regulatory outlook
Stricter AI regulations are expected to address
transparency, data protection, and ethical use.
12. Impact on Cybersecurity Professionals
Generative AI is reshaping cybersecurity careers.
Need for AI literacy
Security professionals must understand AI models,
limitations, and risks.
New job roles and responsibilities
Roles such as AI Security Analyst and ML
Security Engineer are emerging.
Upskilling and training requirements
Continuous learning is essential to stay relevant in
an AI-driven security landscape.
13. Future Outlook
As Generative AI advances, risks will also evolve.
How risks will evolve with GenAI
advancement
More autonomous AI systems may increase both
defensive power and attack sophistication.
Balancing innovation with security
Organizations must innovate responsibly without
compromising security fundamentals.
Responsible AI adoption
Ethical design, governance, and transparency will
define successful AI integration.
Conclusion:
Generative AI in cybersecurity offers immense
potential, but it also introduces significant risks and challenges—from
AI-powered cyber threats and data privacy issues to ethical, legal, and
operational concerns.
A cautious, strategic approach is essential.
Organizations must combine strong governance, human oversight, robust
security frameworks, and continuous monitoring to harness the benefits of
Generative AI safely.
By adopting responsible AI practices, businesses can
strike the right balance between innovation and security, ensuring
long-term resilience in an increasingly AI-driven cyber landscape.