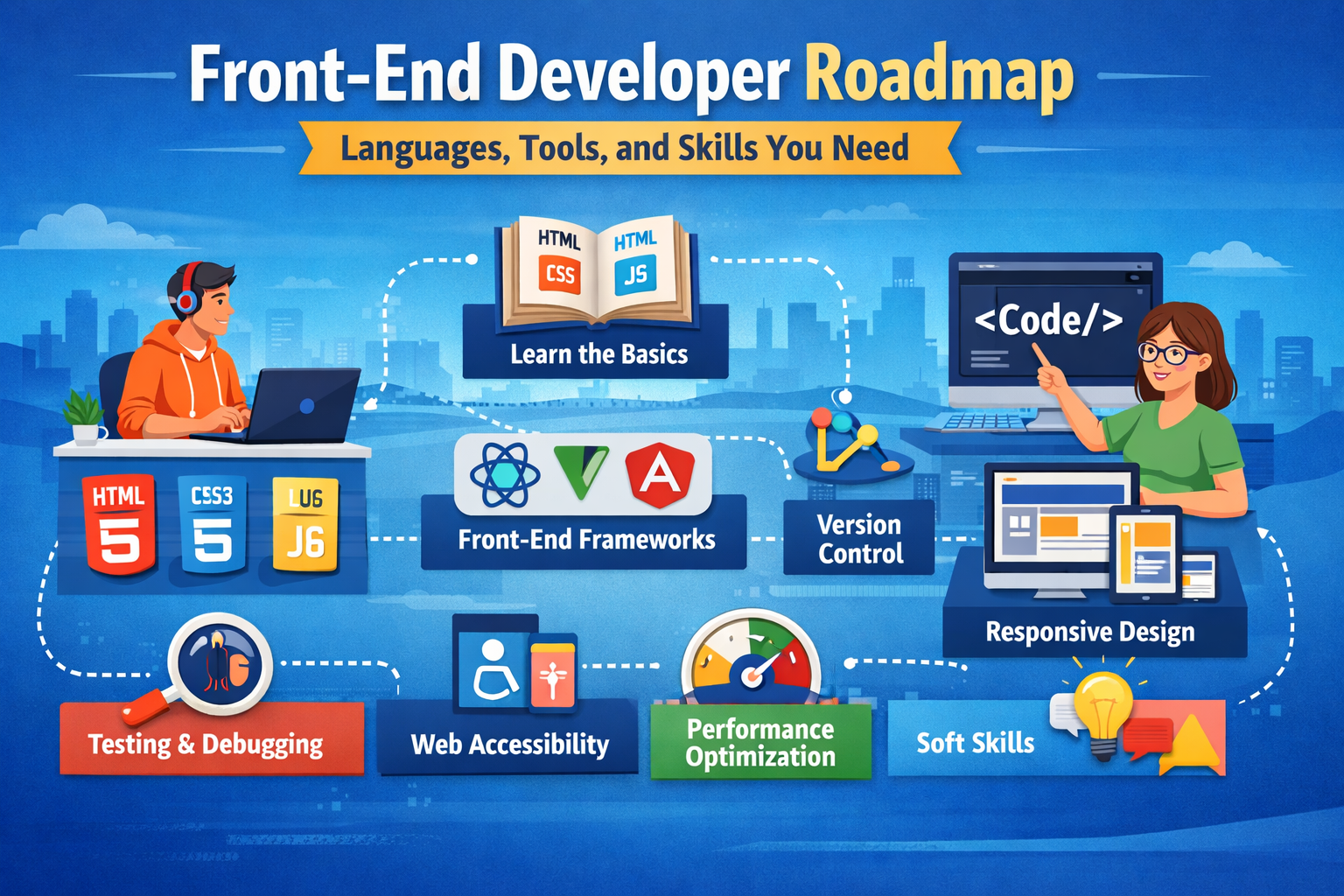
Introduction:
In today’s digital-first world, websites and web
applications are the backbone of businesses, startups, and personal brands.
This is where a front-end developer plays a crucial role. A front-end
developer is responsible for creating everything users see and interact with on
a website, from layouts and buttons to animations and responsive designs.
Front-end development is in high demand due
to the rapid growth of web-based platforms, e-commerce, SaaS products, and
mobile-first experiences. Companies are constantly looking for skilled
professionals who can deliver fast, accessible, and visually appealing user
interfaces.
This Front-End Developer Roadmap will guide
you through the essential languages, tools, frameworks, and skills you
need to become job-ready. Whether you are a beginner, student, or career
switcher, this roadmap will help you plan your learning journey step by step.
Understanding the Front-End Developer
Role:
Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
A front-end developer focuses on the client-side of
web applications. Common responsibilities include:
- Converting
design mockups into functional web pages - Writing
clean, reusable, and maintainable code - Ensuring
websites are responsive across devices - Optimizing
performance and load speed - Implementing
accessibility best practices - Collaborating
with designers and back-end developers
Front-End vs Back-End vs Full-Stack
- Front-End
Developer: Works on UI, UX, and
browser-based interactions - Back-End
Developer: Handles servers, databases, APIs,
and logic - Full-Stack
Developer: Combines both front-end and
back-end skills
Career Opportunities and Growth
Front-end developers can grow into roles such as:
- UI
Engineer - Senior
Front-End Developer - Full-Stack
Developer - Web
Architect - Technical
Lead
Core Front-End Languages
(Must-Learn):
HTML – Structure of the Web
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) forms the
foundation of every website.
Key concepts to learn:
- Semantic
HTML (header, nav, section, article) - Accessibility-friendly
markup - SEO-friendly
structure - Forms
and input validation
Semantic and well-structured HTML improves search
engine rankings and accessibility.
CSS – Styling and Layout
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) controls the visual
appearance of web pages.
Important CSS topics:
- Box
model - Flexbox
and CSS Grid - Responsive
design techniques - Media
queries - CSS
animations and transitions - CSS
preprocessors like SASS
Strong CSS skills are essential for creating modern,
responsive designs.
JavaScript – Interactivity and Logic:
JavaScript brings life to web pages by enabling
dynamic content.
Must-learn JavaScript skills:
- ES6+
features (let, const, arrow functions) - DOM
manipulation - Event
handling - Async
JavaScript (Promises, async/await) - Fetching
APIs
JavaScript is the core language for front-end
development.
Front-End
Frameworks and Libraries:
Why Frameworks Matter
Frameworks help developers build scalable, maintainable
applications faster by providing reusable components and structured
architecture.
React.js – The Most Popular Choice
React.js is widely used due to its performance and
flexibility.
Key React concepts:
- Components
and props - State
management - Hooks
- Virtual
DOM
Vue.js and Angular Overview
- Vue.js:
Beginner-friendly and lightweight - Angular:
Enterprise-level framework with strong structure
Framework vs Vanilla JavaScript
Vanilla JavaScript is ideal for learning
fundamentals, while frameworks are best for large-scale applications.
Version Control and Collaboration
Tools:
Git Basics
Git helps track code changes and collaborate
efficiently.
Essential Git commands:
- git
init - git
commit - git
branch - git
merge
GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket
These platforms allow you to host repositories,
collaborate with teams, and showcase your portfolio.
Team Workflows
Understanding pull requests, code reviews, and
branching strategies is essential for real-world projects.
Development Tools Every Front-End Developer
Needs:
Code Editors
- Visual
Studio Code (VS Code) is the most popular editor - Extensions
improve productivity and debugging
Browser Developer Tools
DevTools help inspect elements, debug JavaScript,
and test performance.
Package Managers
- npm
- yarn
They manage libraries and dependencies efficiently.
Build Tools
- Vite
- Webpack
Build tools optimize and bundle your code for
production.
Responsive Design and Cross-Browser
Compatibility:
Mobile-First Design
Designing for mobile devices first ensures better
user experience.
Media Queries
Media queries allow layouts to adapt to different
screen sizes.
Browser Testing Tools
Testing ensures consistency across Chrome, Firefox,
Safari, and Edge.
Performance Optimization Skills:
Performance directly impacts user experience and
SEO.
Key optimization techniques:
- Code
splitting and lazy loading - Image
compression - Reducing
unused CSS and JavaScript - Understanding
Core Web Vitals (LCP, CLS, FID)
Web Accessibility (A11y):
Accessibility ensures your website is usable by
everyone.
Important accessibility practices:
- Follow
WCAG guidelines - Enable
keyboard navigation - Use
ARIA roles correctly - Maintain
color contrast
Accessible websites perform better in search
rankings and user trust.
Testing and Debugging:
Unit Testing Basics
Testing helps catch bugs early and ensures
reliability.
Testing Tools
- Jest
for unit testing - Cypress
for end-to-end testing
Debugging Best Practices
Use browser tools, console logs, and breakpoints
effectively.
Soft Skills for Front-End Developers:
Technical skills alone are not enough.
Essential soft skills include:
- Communication
with designers and back-end teams - Problem-solving
mindset - Time
management - Adaptability
to new technologies
Building Projects and
Portfolio:
Project Ideas:
- Personal
portfolio website - Responsive
landing pages - To-do
apps - E-commerce
UI - Dashboard
interfaces
GitHub Portfolio Tips:
- Write
clean README files - Use
meaningful commit messages - Showcase
real-world projects
Live Demos and Case Studies:
Live projects increase credibility and job
opportunities.
Learning Timeline and Career
Path:
0–3 Months: Fundamentals:
- HTML,
CSS, JavaScript basics - Responsive
design - Git
and GitHub
3–6 Months: Frameworks and Projects:
- Learn
React or Vue - Build
multiple projects - Focus
on performance
6–12 Months: Advanced Skills:
- Accessibility
and testing - Optimization
techniques - Job
preparation and interviews
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Skipping
HTML and CSS fundamentals - Over-relying
on frameworks - Ignoring
accessibility - Neglecting
performance optimization
Conclusion:
This Front-End Developer Roadmap provides a
clear and structured path to mastering the languages, tools, frameworks, and
skills required to succeed in modern web development. By focusing on
fundamentals, building real projects, and continuously learning, anyone can
become a skilled front-end developer.
Next Steps
- Start
with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript - Build
small projects consistently - Learn
a framework like React - Create
a strong portfolio
With dedication and practice, your journey into
front-end development can lead to a rewarding and future-proof career.